i always thought /usr stood for "user". Please tell me I'm not the only one
Linux
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Linux is a family of open source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991 by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically packaged in a Linux distribution (or distro for short).
Distributions include the Linux kernel and supporting system software and libraries, many of which are provided by the GNU Project. Many Linux distributions use the word "Linux" in their name, but the Free Software Foundation uses the name GNU/Linux to emphasize the importance of GNU software, causing some controversy.
Rules
- Posts must be relevant to operating systems running the Linux kernel. GNU/Linux or otherwise.
- No misinformation
- No NSFW content
- No hate speech, bigotry, etc
Related Communities
Community icon by Alpár-Etele Méder, licensed under CC BY 3.0
Ken Thompson and Dennis Ritchie created Unix on a PDP-7 in 1969. Well around 1971 they upgraded to a PDP-11 with a pair of RK05 disk packs (1.5 megabytes each) for storage.
When the operating system grew too big to fit on the first RK05 disk pack (their root filesystem) they let it leak into the second one, which is where all the user home directories lived (which is why the mount was called /usr). They replicated all the OS directories under there (/bin, /sbin, /lib, /tmp...) and wrote files to those new directories because their original disk was out of space. When they got a third disk, they mounted it on /home and relocated all the user directories to there so the OS could consume all the space on both disks and grow to THREE WHOLE MEGABYTES. And thereafter /usr is used to store user programs while /home is used to store user data.
source: http://lists.busybox.net/pipermail/busybox/2010-December/074114.html
THREE WHOLE MEGABYTES
Me in 2024 holding a 4TB NVMe stick: Still not enough (it's never enough)
You're not the only one 😅 🙋
I thought it was United System Resources.
And I still don't know what's the point in separating /bin, /sbin, /usr/bin and /usr/sbin.
Also /mnt and /media
Or why it's /root and not /home/root
Mostly historical reasons, /home was often a network mounted directory, but /root must be local.
And only regular users have their home in /home
/home is often on a separate volume. You’d want root to be available in a maintenance situation where /home may not be mounted.
I don't recall the reasons for the addition but /media is newer than /mnt.
And I still don't know what's the point in separating /bin, /sbin, /usr/bin and /usr/sbin.
This goes back to the olden days when disk space was measured in kilo and megabytes. /sbin/ and /usr/sbin have the files needed to start a bare bone Unix/Linux system, so that you could boot from a 800kb floppy and mount all other directories via network or other storage devices as needed.
They hold "system binaries" meant for root user. It's not a hard distinction but many if not most Linux fundamentals have their roots in very early computing, mainframes, Bell and Xerox, and this good idea has been carried into the here&now. Not sure about the provenance of this one, but it makes sense. isn't /mnt /media different between distros? These aren't hard and fast rules - some distros choose to keep files elsewhere from the "standard".
/bin and /usr/bin, one is typically a symbolic link to another - they used to be stored on disks of different size, cost, and speed.
https://refspecs.linuxfoundation.org/FHS_3.0/fhs/ch03s16.html
https://unix.stackexchange.com/questions/5915/difference-between-bin-and-usr-bin
I think it originally did under old Unix, it was what /home is nowadays; "Unix System Resources" is a backronym.
It's always been for USeR binaries. It's the first time I've seen this bizarre backronym (40 years of Unix here).
"Linux File Systems"
*List of root directories*
Uh, where are the file systems? EXT4... BTRFS... FAT32...
That’s what I thought too. This is directory structure, not file systems.
https://lemmy.world/post/9437525
My version of this with a bit more detail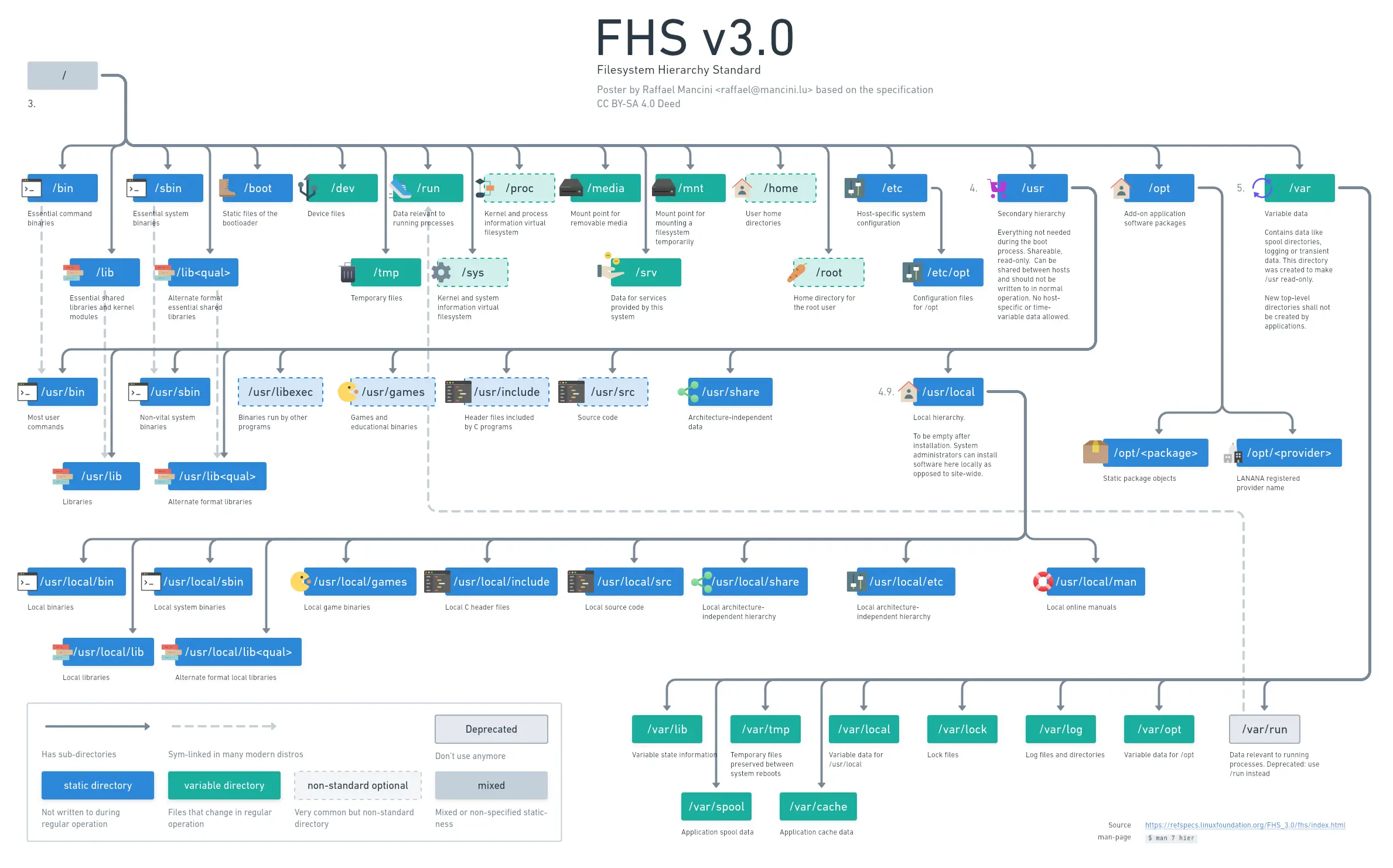
I don’t get why this sort of picture always gets posted and upvoted when it’s wrong for most distros nowadays.
Can you recommend one that is correct? I use pop_os (Ubuntu) and Arch. Kinda curious about either one
Not aware of any correct pictures, but I can tell you what's wrong with this one
- /usr: explaining it as "Unix System Resources" is a bit vague
- /bin: /bin is usually a symlink to /usr/bin
- /sbin: /sbin is usually a symlink to /usr/sbin, distros like Fedora are also looking into merging sbin into bin
- /opt: many, I'd say most, "add-on applications" put themselves in bin
- /media: /media is usually a symlink to /run/media, also weird to mention CD-ROMs when flash drives and other forms of storage get mounted here by default
- /mnt: i would disagree about the temporary part, as I mentioned before, stuff like flash drives are usually mounted in /run/media by default
- /root: the root user is usually not enabled on home systems
- /lib: /lib is usually a symlink to /usr/lib
I would also like the mention that the FHS standard wasn't designed to be elegant, well thought out system. It mainly documents how the filesystem has been traditionally laid out. I forget which folder(s), but once a new folder has been made just because the main hard drive in a developer's system filled up so they created a new folder named something different on a secondary hard drive.
wait /usr doesn't mean user?
/etc has to be the worst name in there
usr does mean user. It was the place for user managed stuff originally. The home directory used to be a sub directory of the usr directory.
The meaning and purpose of unix directories has very organically evolved. Heck, it's still evolving. For example, the new .config directory in the home directory.
For example, the new .config directory in the home directory.
I hope slowly but surely no program will ever dump its config(s) as ~/.xyz.conf (or even worse in a program specific ~/.thisapp/;
The ~/.config/ scheme works as long as the programs don't repeat the bad way of dumping files as ~/.config/thisconfig.txt. (I'm looking at you kde folks..) A unique dir in .config directory should be mandatory.
If I ever need to shed some cruft accumulated over the years in ~/.config/ this would make it a lot easier.
I wonder why that isn't /cfg? Is there a historical reason?
According to this, it's been around since the 70's and was originally just a catch-all for files that didn't fit in the other default directories, but over time has come to be mostly used for config files. I assume it would cause utter mayhem to try and change the name now so I guess it just sticks. Someone suggested "Edit To Configure" as a backronym to try and make it make more sense if that helps anyone lol.
Is there a historical reason?
If you're asking that in anything Linux related, it's probably a Yes 99% of the time LMAO
I learned about 16 years ago on a Solaris course that /usr wasn't "user", I still say "user", but I'm happy to see the information spreading that that isn't what it actually is.
usr did originally mean user and held user data.
Pretty sure this is a bacronym
/home is for every program to store its personal junk in hidden files apaprently
A pedantic thing to say, surely, but the title really should've been: "Linux Directory Structure" -- 'Linux filesystems' (the title in the graphic) refers to a different topic entirely; the title of this post mitigates the confusion a bit, though still, 'directory structure' is the better term.
To be more pedantic the correct title would be the Filesystem Hierarchy Standard (FHS)...which describes the directory structures
/opt/(app)/bin /usr/lib/(app)/bin /usr/lib64/app/bin /usr/local/(s)bin
I know there is logic and mapping of where everything's supposed to be in theory but in practice s***'s kind of all over the place.
The logic was just that when UNIX was originally evolving, they ran out of disk space on their PDP-11 and had to start moving less-essential binaries to a different disk. That's why it's "/usr/" which was originally for user data but that disk happened to have free space.
Any other explanation is just retcon. Some distros try to simplify things.
I always thought /usr was for "user".... TIL
It is, this infographic is wrong. Or I guess technically some other standard could define it like the infographic, but the Filesystem Hierarchy Standard defines it as a secondary hierarchy specifically for user data.
It did, let me explain:
On the original (ie Thompson and Ritchie at Bell in 1969-71), I think it was a PDP-11, they installed to a 512kb hard disk.
As their "stuff" grew they needed to sprawl the OS to another drive, so they mounted it under /usr and threw OS components that didn't fit.
https://landley.net/writing/unixpaths.pdf
I've done the same, outgrew so you mount under a tree to keep going, it just never became a historical artifact.
A good first approximation.
So where in this setup would you mount a network share? Or am additional hard drive for storage? The latter is neither removable nor temporary. Also /run is quite more than what this makes it seem (e.g. user mounts can be located there), there is practically only one system path for executables (/usr/bin)...
Not saying that the graphic is inherently wrong or bad, but one shouldn't think it's the end all be all.
I never understood the title for /usr. Now I do. Thanks!
I always thought it stood for user. I even say it that way.
Those are directories, not filesystems.
It feels like /opt 's official meaning is completely lost on developers/packagers (depending on who's at fault), every single directory in my /opt belongs to standalone software that should just be put into either /usr/lib or /usr/share with some symlinks or scripts into /usr/bin.
Fun fact: you get more accurate info by simply running man hier
I'm pretty sure sbin originally meant static binaries and not system binaries lol
Visualizing it like this makes it so clear how incredibly outdated this design is.
Would like an easy way to remember.
- mnt = mount
- opt = optional ?
- etc = etcetera ?
- proc = process ?
- srv = server ?
- var = variable ?
