this post was submitted on 10 Apr 2024
642 points (98.9% liked)
Memes
9615 readers
2045 users here now
Post memes here.
A meme is an idea, behavior, or style that spreads by means of imitation from person to person within a culture and often carries symbolic meaning representing a particular phenomenon or theme.
An Internet meme or meme, is a cultural item that is spread via the Internet, often through social media platforms. The name is by the concept of memes proposed by Richard Dawkins in 1972. Internet memes can take various forms, such as images, videos, GIFs, and various other viral sensations.
- Wait at least 2 months before reposting
- No explicitly political content (about political figures, political events, elections and so on), [email protected] can be better place for that
- Use NSFW marking accordingly
Laittakaa meemejä tänne.
- Odota ainakin 2 kuukautta ennen meemin postaamista uudelleen
- Ei selkeän poliittista sisältöä (poliitikoista, poliittisista tapahtumista, vaaleista jne) parempi paikka esim. [email protected]
- Merkitse K18-sisältö tarpeen mukaan
founded 2 years ago
MODERATORS
you are viewing a single comment's thread
view the rest of the comments
view the rest of the comments

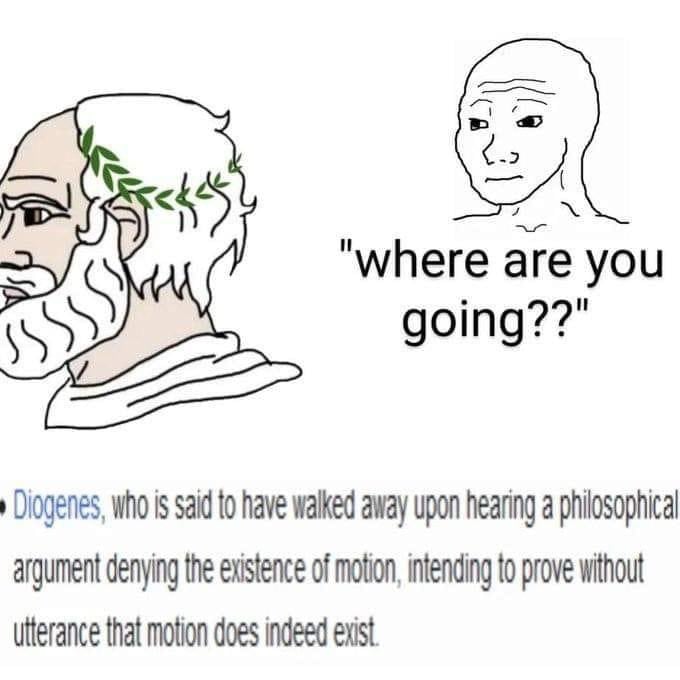
Reminds me of the G.E. Moore epistemological argument against universal skepticism:
Philosophy sometimes goes so far that an appeal to common sense is a breath of fresh air.
The conclusion in line three does not follow from the premises in lines one and two, because perception is not reality.
The correct argument against universal skepticism:
As usual, the only persuasive argument in favour of realism is "might makes right", accompanied by persecution of the antirealists.
The argument makes less sense outside of it's context. Moore was responding to the skeptical position that we're all in a simulation. Moore argues that this skeptical argument undermines itself: all of the language, terms and concepts which form the simulation argument are based on the sensory experience that the argument would effectively dismiss. Furthermore, any argument that we're in a simulation is epistemologically on a par with the argument that we're not. Therefore we should have less confidence in the skeptical argument than the common sense conclusion that we have hands.
The point about "are we in a simulation?" is not that we are (setting aside the whole technological singularity thing for the moment), but that we could be. The common sense thing only says that we're more likely not, but does not at all say that we definitely are not. "Could be" still remains.
Moore's point is that we shouldn't let the inability to eliminate that "what if," which was specifically designed to be non-disprovable, actually affect ontology. That problems and questions created by philosophers basically just to stump philosophical methods should be all but ignored since, by design, there clearly can't be an answer except that one thing is by far most likely, and the other thing cannot matter because we can't prove or act upon it or treat it as anything other than a manufactured source of doubt/skepticism.
It is still important to understand that the only thing which can be known about reality with complete certainty is:
We cannot know with certainty the nature of that reality. We can only know our perception, and even if we accept that we are perceiving reality (which is most likely, but not necessarily, true), our perceptions of that reality are incomplete and flawed. That's a pretty important part of the nature of being.
Objective reality doesn't exist, and that's a good thing, because it means our entire universe is subjective, and therefore, malleable to our perceptions. It means that with a big enough idea and a mind on which to balance it, we can move the earth.
I think, therefore I am. An objective reality exists, because you exist. The question is, how much of reality can you perceive, and to what limit?
My existence is subjective. Therefore any reality whose existence is assumed on my basis is also subjective.
That's because you're afraid to have an intellectually honest discussion with someone who disagrees with you. It's easier to pretend people who disagree with you don't exist.
The fact that the self is an illusion is not a new idea. Surely you've heard of it. But you'd rather pretend that I don't believe in it than to have an actual conversation considering its implications.
Western neurotypicals are so very concerned with ego. It's unhealthy.
Can you show me a moment of this discussion when I was "obnoxious" from before you insulted me? Cause I wanted to have an actual discussion, and you're saying you do as well, but what you're saying would be hard to believe if you were the first one to throw an insult in place of a discussion.
Nah, this is bullshit. What sensory experience is love? What sensory experience is honour? And more to the point, what sensory experience is money? Is law? Is a home? Is a mother? If Moore were correct to say that we do not live in a constructed material reality, we would still live in a constructed social reality. And if social reality can be constructed without the aid of the senses, then it must also be true that material reality can be constructed without the senses.
Moore is clearly a simpleton.
I disagree with Moore's first point. Hands are a social construct and are not imbued with inherent reality. They gain reality only when observed by a conscious agent.
I get rather irritated with those arguments because they only return to the start. "Here, a world". "Is it how we experience it, though, and why and how; if not, what's behind?". "Bullshit, a world". That's hardly an answer. And, personally, it feels intellectually dishonest because the question was larger than just "is there a world?".
I prefer an answer like saying that doubting the world in any form might be a mistake on its own because [reasons]. I do not agree, but at least there's explanations and communication.
Also, I think they are fighting a straw man. For instance, I doubt many things about the Universe, our knowledge, our minds, etc. Yet, I accept there are phenomena which appear to me. This has been the case since the ancient school of skepticism, and I have yet to meet a person which declares themself a skeptic and does not do this to some degree. For example, I know I'm hungry right now. I don't know if the pain is real in any other deeper level, or if it is like the pain in a dream that goes away when one wakes up, or a delusion that is felt without external stimuli, or whatever. I don't know the nature of it, yet it is an experience I must attend. I can even add that the mechanisms behind, the anatomical knowledge and such is useful, but it might be entirely wrong or be as illusory as the pain itself. The straw man is that skeptics would say: "I don't know if I'm really feeling hungry", "I don't know if I want to eat" or something like that.
Why does it matter, then? Because it changes everything. In my case, it made me go from a realist teenager to an instrumentalist adult in science. From an atheist teenager to an agnostic adult.
The discussion derives in many interesting branches too. The mere "does it matter if the world is different from what we perceive if we cannot perceive it in any other way?" is an example. Many people answer yes or no without justifying it. And, at this point, some people might be wondering why we need to justify every single belief we hold and every single thing we say, like the ones throughout my comment, and that in itself is a new good question that emerges. The possibility of having any of these conversations is also a good question, and so on...
So philosophy is not going too far, in my opinion. Some philosophers might go too far, but I really think they are rare (or misunderstood).