Like others said an Intel CPU with iGPU, alternatively the cheapest Intel Arc GPU (A380?) supports the latest spec of Intel QSV as well.
Selfhosted
A place to share alternatives to popular online services that can be self-hosted without giving up privacy or locking you into a service you don't control.
Rules:
-
Be civil: we're here to support and learn from one another. Insults won't be tolerated. Flame wars are frowned upon.
-
No spam posting.
-
Posts have to be centered around self-hosting. There are other communities for discussing hardware or home computing. If it's not obvious why your post topic revolves around selfhosting, please include details to make it clear.
-
Don't duplicate the full text of your blog or github here. Just post the link for folks to click.
-
Submission headline should match the article title (don’t cherry-pick information from the title to fit your agenda).
-
No trolling.
Resources:
- awesome-selfhosted software
- awesome-sysadmin resources
- Self-Hosted Podcast from Jupiter Broadcasting
Any issues on the community? Report it using the report flag.
Questions? DM the mods!
A310 is the cheapest.
I wonder how well it does for transcoding on older computers without ReBAR, since apparently gaming on it is straight out broken without ReBAR. As in, it would actually freeze for a second or so every now and then.
Encoding engine basically requires it, so you'd need to implement a hack or something. https://www.reddit.com/r/IntelArc/comments/189cgsm/intel_arc_h265_encoding_performance_and_resizable/
You can enable REBAR on older machines with a UEFI hack.
It's been part of the PCI spec for ages but Nvidia and AMD only started using it recently.
You can easily do smooth 4K HDR transcoding with any modern Intel CPU with integrated graphics.
I have an Intel N100 and it can probably handle 2-3 4K HDR transcodes at once. Definitely more if they're being transcoded down to lower resolutions. Encoding is the most intensive part of the process.
Intel GPUs look like a great value. And AV1 hardware acceleration is a game changer
Read up on Intel QSV. You essentially only need a recent cpu. i3 would do.
GPU all the way as it will be more efficient. Keep in mind Intel integrated graphics counts as a GPU
One of my miniPCs is just a little N95 and it can easily transcode 4K HDR to 1080p (HDR or tonemapped SDR) to a couple of clients, and with excellent image quality. You could build a nice little server with a modern i3 and 16gigs of ram and it would smash through 4 or 5 high bitrate 4K HDR transcodes just fine.
Is that one transcoding client local to you? or are you trying to stream over the web? if it's local, put some of the budget to a new player for that screen perhaps?
I tried that with a cheap minipc I bought and it was CPU limited. The GPU was fine it was the overhead that killed me.
Was it an n100? They have a severely limited power budget of 6w compared to the n95 at 25w or so.
I'm running jellyfin ontop of ubuntu desktop while also playing retro games. That all sits in a proxmox vm with other services running alongside it. It's perfectly snappy.
I believe it is N9505 if I remember correctly. It is also possible I didn't give it enough cores.
N5095 ? lots of reports of that one not supporting everything it should based on other Jasper Lake chips, CPU getting hit for Decode when it shouldn't for example. Also HDR to SDR cant be accelerated with VPP on that one as far as I know so the CPU gets smashed. I think you can do it with OpenCL though.
Curious: What's the deal with all the transcoding on servers?
Don't you just need some good rendering on the client? And if you need it on the server, why need it on the fly? You can do it before, and store the result, can't you?
Compatibility and storage.
Do you want only 2 devices of the 10 your family possibly owns to work?
Do you want your family to complain that jellyfin "isn't as good as Netflix/Disney+/etc.." Because it constantly stops to buffer and a can't keep up the framerate?
It is completely fine if you are single and have 1-2 devices that work with AV1 and h.265 client side and that is all you need, then you don't have to bother with transcoding at all. When you start letting other people into it, compatibility becomes an issue.
As for storing it beforehand, the entire point of AV1 and HEVC is to significantly reduce the size on disk. If you have to store 10 versions or each file, 5 resolutions each, half h.264, then you are taking up about 20x the space per file compared to 1 copy of HEVC or AV1.
A transcode GPU like the A380 or new QSV compatible CPU is MUCH cheaper than a new good quality 12TB drive lol
Sorry for the long text, it pretty much depends on the living situation.
Very much agree on all these points; I just wish I could get the transcoding to actually work.
I’ve been running Jellyfin in a container and giving it access to an old GTX970 but it just refuses to do anything with it.
The 970 unfortunately doesn't have h265 hardware in it. The only gpu in that generation that does is the 960, as it was released later than the others and was one of the first to get h265. I ended up just getting a p400, and it's been rock solid.
The 970 works for encoding h.264 only. My recommendation: If you have a 7th Gen Intel CPU with iGPU or later, use that. Otherwise, sell the 970 and get one of these (in this order):
- Intel Arc A310
- GTX 1650
- GTX 1630
- Quadro P1000
- Quadro T400
- GTX 1050 Ti
- GTX 1050
- Quadro P620
- Quadro P600
- Quadro P400
The Intel Card has the best encoder, followed by Nvidia Turing, then Pascal. I recently sold my 970 and got a 1050 Ti for the same price. Works great with Jellyfin. If you need to tone map HDR, you probably shouldn't get anything with much lower performance than that. If it's just some UHD to HD or h.265 to h.264 for compatibility, even the P400 will work well.
thanks for the tips! I am running a Ryzen 9 5950X, so it definitely needs a standalone GPU. I am going to be getting a 1070 off the kids’ computer once I upgrade them later this year, so I think I’ll just stick that into it.
Would really like to get the seamless transcoding to work so the whole family can use it without hiccups.
A few reasons.
For one, storing multiple versions of the same film takes up a lot of storage, which is more expensive than a cheap 40€ gpu for transcoding. And I definitely wanna keep the highest quality I can. Besides transcoding on the fly is more flexible, ensuring the best possible quality at any time, instead of having to pick between the good and the shit version.
And secondly, usually I only need transcoding when I don’t watch on my home setup (or when some friends watch on my server). My upload isn’t as high as some of my film’s bitrates and some clients do not support h.265 or HDR thus needing transcoding and/or tonemapping.
The mobile and TV clients are often limited to the codecs with hardware acceleration. Or just selecting a lower bitrate on the client will cause transcoding.
People talk about the cost of storage space but neglect the cost of electricity to constantly transcode video files. And it’s not like the output is saved for the next time; you need to do it every time.
Plus, I’d bet most people sit too far from their TV to be able to see the actual different between 1080p and 4k.
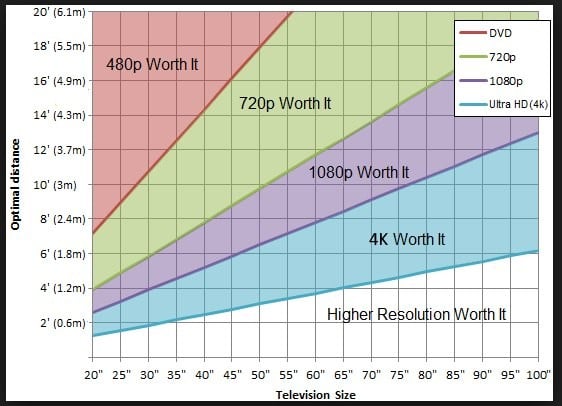
HDR? Sure. But 4k? Doubtful.
I keep two libraries - one that’s 720/1080p and a second that’s 4k only. My 4k content is severely limited to only things I REALLY want in 4k.
And it’s not like the output is saved for the next time; you need to do it every time.
You can cache transcoded content in Jellyfin. So use a large enough cache and you basically only have to transcode once for every resolution. It's easier for me to set up transcoding than it would be to manually figure out which resolutions I'll prefer having around and transcoding them. Most of my stuff exists in 1080p, with 4k files for stuff I REALLY like, but I sometimes find myself watching on very low resolutions on my phone when away because I have pretty limited data.
I find that in a few movies the 4K versions have a generally better image quality and are worth it even if you are sitting far away or not watching the content in 4K resolution at all. But like you, I only keep around 4k files for stuff I really like.
EDIT: I've also run into problems with codecs on other people's devices when not transcoding. I could keep my files in whatever the most compatible codec is nowadays but having the ability to transcode on the spot is easier.
The easiest and cheapest solution is don’t allow transcoding.
The easiest way to do that is separate your 720/1080p videos from your 4k videos. Limit 4k access to the users that can play 4k
I've been trying to get this to work for weeks now. No dice, so far. Anybody know any useful guide on setting it up for a docker installation? Or does it only work if you install the.deb? I use Mint, BTW. Server is a Dell with a 9th gen i5.
I also struggled to get it to work with an Intel Celeron N5100. To get it to work I followed the instructions in the Jellyfin documentation. It seems like there are some additional steps for some versions of Intel CPUs, could it be that yours is affected? After enabling "Low-Power Encoding" it worked as expected.
Do you have it installed with docker?
Yes, I have it installed as a Docker container in a Debian 12 machine. My Docker compose file is something like this:
jellyfin:
container_name: jellyfin
image: jellyfin/jellyfin
group_add:
- "105"
- "44"
- "102"
devices:
- /dev/dri/renderD128:/dev/dri/renderD128
- /dev/dri/card0:/dev/dri/card0
The group numbers were obtained following Jellyfin's documentation.
You also need to configure Jellyfin from Menu > Playback. In "Hardware acceleration" I selected "Intel QuickSync (QSV)". I have selected all but AV1 (not supported by my CPU) from "Enable hardware decoding from:" and from "Hardware encoding options:" I have enable all 3 of them.
What specifically isn't working? I've got Jellyfin running on Docker with transcoding from a Nvidia GPU.
I pretty much followed the documentation here: https://jellyfin.org/docs/general/administration/hardware-acceleration/nvidia. I can share my docker-compose for that specific use case if you'd like.
"jellyfin-ffmpeg5 deb package" is one bit I'm confused about. Is that part of the docker installation? If not, if I install the deb, can the docker installation use it? Do I have to configure something there?
Check the Jellyfin wiki
I think those miniPC CPUs do a good job transcoding from what I've read, the N95 and N100. I already had older hardware set up when I added Jellyfin so I got a cheap nvidia Quadro P400 for the transcoding. If you're setting up a new system though, I'd guess a Intel iGPU would be more than enough.
I've looked at https://www.elpamsoft.com/?p=Plex-Hardware-Transcoding before for transcoding comparisons.
I have no idea what the people who recommend CPU are smoking. The difference between a GPU with hardware support and doing it on the CPU is huge.
It’s really not, like at all. QuickSync is fast af and overkill for almost any usecase.
Setups for hardware decoding are based on the underlying OS. An example quite common is docker on Debian or Ubuntu. You will need to pass the appropriate /dev/ directories and at times files into your jellyfin docker container with the device environment variable. Commonly that would be /dev/dri
It gets more complicated with a vm because you are likely going to be passing the hardware directly into the vm which will prevent other devices outside the vm from using it.
You can get around this by placing docker directly on the os or placing docker in a Linux container with appropriate permissions and the same devices passed into the Linux container. In this manner system devices and other services will still have access the the video card.
All this to say it depends on your setup and where you have docker installed how you will pass the hardware into jellyfin. However jellyfin on docker will need you to pass the video card into the container with the device environment variable. Docker will need to see the device to be able to do that.
I've been using podman due to its low overhead.
Nothing but love for that project. I've been using docker-ce and docker-compse. I had portainer-ce but just got tired of it. It's easier for me to just make a compose file and get things working exactly like I want.
My optiplex with i5-6500TE can transcode 4K videos easily if the codec is AVC. HEVC is different story though. Any CPU newer than 10th generation would be more than enough for your needs, I'd say.
My current setup:
- one stream using CPU transcoding, Intel Xeon E2246G
- six streams using GPU transcoding, Nvidia Tesla P4
If only 1 person will watch at any given time, cpu is plenty